Compare changes
+3
−2
+168 KiB
167.77 KiB
+194 KiB
194.01 KiB
+179 KiB
179.28 KiB
+100 KiB
100.35 KiB
+16.1 KiB
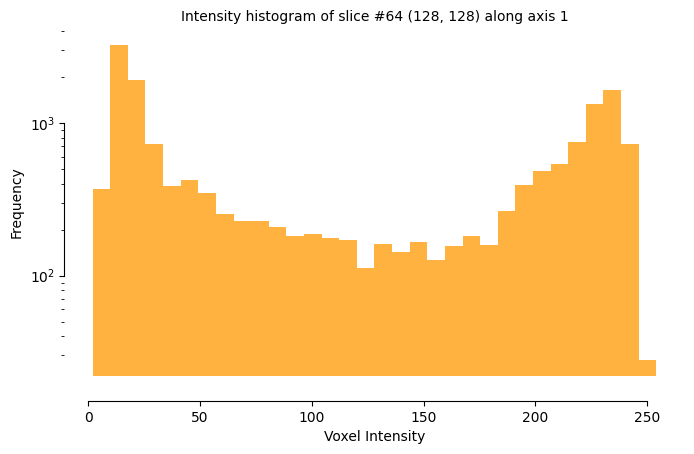
16.14 KiB
+31.9 KiB
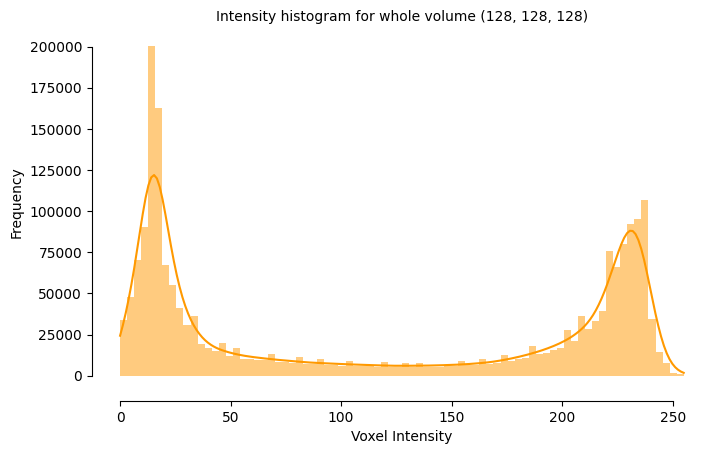
31.87 KiB
+34.8 KiB
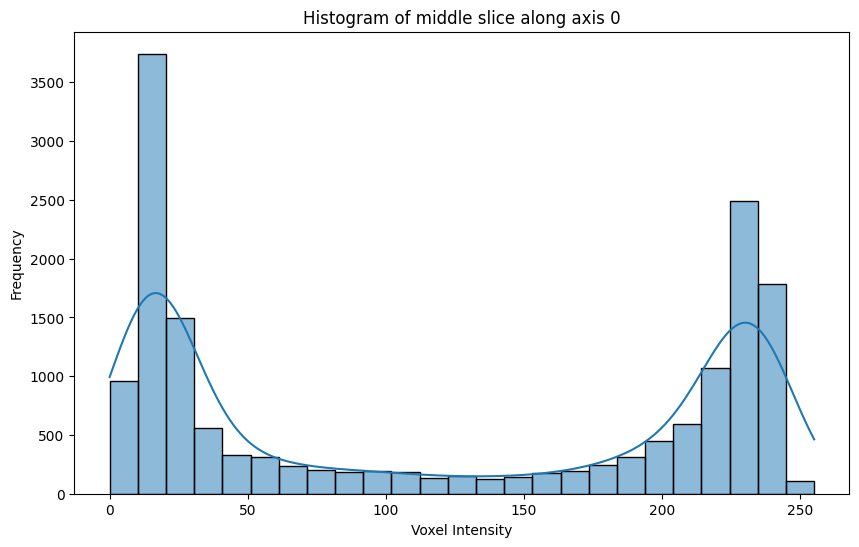
34.78 KiB
+1
−1
+21
−9
+8
−0
+1
−0
+2
−2
+1
−1
+2
−2
+101
−4
+70
−37
+1
−1
+2
−2
+9
−1
+1
−1
+1
−0
+8
−2
+183
−16
+36
−6